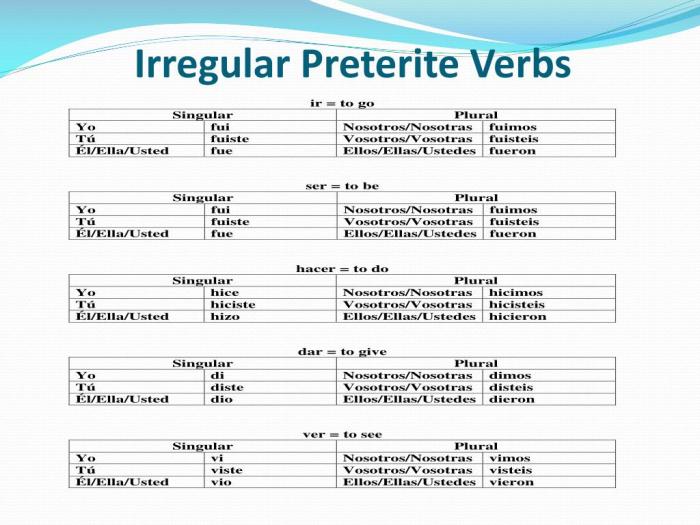
Gramatica a irregular verbs in the preterite – Delving into the realm of grammar, the concept of irregular verbs in the preterite tense takes center stage. These verbs, with their unique and often unpredictable conjugations, can pose a challenge for language learners. However, understanding their formation, usage, and common pitfalls is essential for effective communication.
Irregular verbs in the preterite tense, also known as the simple past tense, are those that do not follow the regular patterns of verb conjugation. Their unique forms must be memorized to ensure accurate and fluent speech.
Irregular Verbs in the Preterite Tense
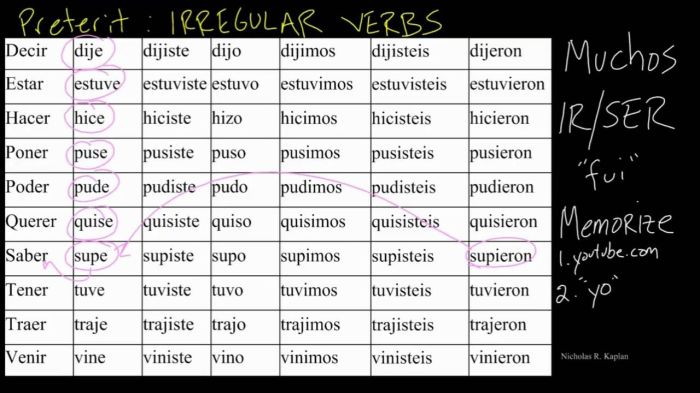
In the English language, irregular verbs are those that do not follow the regular rules for forming the preterite tense (past tense). These verbs have unique past tense forms that must be memorized.
Definition of Irregular Verbs in the Preterite Tense
Irregular verbs in the preterite tense are verbs that have a different form in the past tense than the regular -ed ending. For example, the verb “go” has the preterite tense form “went”, while the verb “run” has the preterite tense form “ran”.
There are many irregular verbs in the English language, and they can be difficult to learn. However, there are some general rules that can help you to identify irregular verbs.
Formation of Irregular Verbs in the Preterite Tense, Gramatica a irregular verbs in the preterite
There are no set rules for forming the preterite tense of irregular verbs. However, there are some general patterns that can help you to learn them.
- Many irregular verbs change their vowel in the preterite tense. For example, the verb “eat” has the preterite tense form “ate”, and the verb “drink” has the preterite tense form “drank”.
- Some irregular verbs add a consonant to the end of the verb in the preterite tense. For example, the verb “keep” has the preterite tense form “kept”, and the verb “get” has the preterite tense form “got”.
- Some irregular verbs change their spelling completely in the preterite tense. For example, the verb “be” has the preterite tense form “was”, and the verb “have” has the preterite tense form “had”.
The following table provides a list of some common irregular verbs and their preterite tense forms:
| Verb | Preterite Tense |
|---|---|
| be | was/were |
| become | became |
| begin | began |
| break | broke |
| bring | brought |
| buy | bought |
| catch | caught |
| choose | chose |
| come | came |
| do | did |
| drink | drank |
| drive | drove |
| eat | ate |
| fall | fell |
| feel | felt |
| find | found |
| fly | flew |
| get | got |
| give | gave |
| go | went |
| have | had |
| hear | heard |
| hold | held |
| hurt | hurt |
| keep | kept |
| know | knew |
| leave | left |
| lend | lent |
| let | let |
| lie | lay |
| lose | lost |
| make | made |
| meet | met |
| pay | paid |
| put | put |
| read | read |
| ride | rode |
| ring | rang |
| run | ran |
| say | said |
| see | saw |
| sell | sold |
| send | sent |
| set | set |
| shake | shook |
| show | showed |
| shut | shut |
| sing | sang |
| sit | sat |
| sleep | slept |
| speak | spoke |
| spend | spent |
| stand | stood |
| steal | stole |
| stick | stuck |
| strike | struck |
| swear | swore |
| swim | swam |
| take | took |
| teach | taught |
| tell | told |
| think | thought |
| throw | threw |
| understand | understood |
| wake | woke |
| wear | wore |
| win | won |
| write | wrote |
Usage of Irregular Verbs in the Preterite Tense
Irregular verbs in the preterite tense are used to describe actions that happened in the past. They are used in both spoken and written English.
Here are some examples of sentences using irregular verbs in the preterite tense:
- I went to the store yesterday.
- She ate a sandwich for lunch.
- He drove to work every day.
- We saw a movie last night.
- They got married last year.
The preterite tense is often used in conjunction with the simple past tense. The simple past tense is used to describe actions that happened in the past that are not connected to the present. The preterite tense is used to describe actions that happened in the past that are connected to the present.
Common Mistakes in Using Irregular Verbs in the Preterite Tense
One of the most common mistakes that learners of English make is using the regular -ed ending for irregular verbs in the preterite tense. For example, instead of saying “I went to the store yesterday”, they might say “I goed to the store yesterday”.
Another common mistake is using the present tense form of the verb for the preterite tense. For example, instead of saying “She ate a sandwich for lunch”, they might say “She eats a sandwich for lunch”.
To avoid these mistakes, it is important to memorize the irregular forms of the verbs in the preterite tense.
FAQs: Gramatica A Irregular Verbs In The Preterite
What is the difference between regular and irregular verbs in the preterite tense?
Regular verbs follow predictable conjugation patterns, while irregular verbs have unique forms that must be memorized.
How can I avoid making mistakes when using irregular verbs in the preterite tense?
Practice regularly, memorize the irregular forms, and consult reliable grammar resources.
When should I use the preterite tense?
The preterite tense is used to describe completed actions or events in the past.